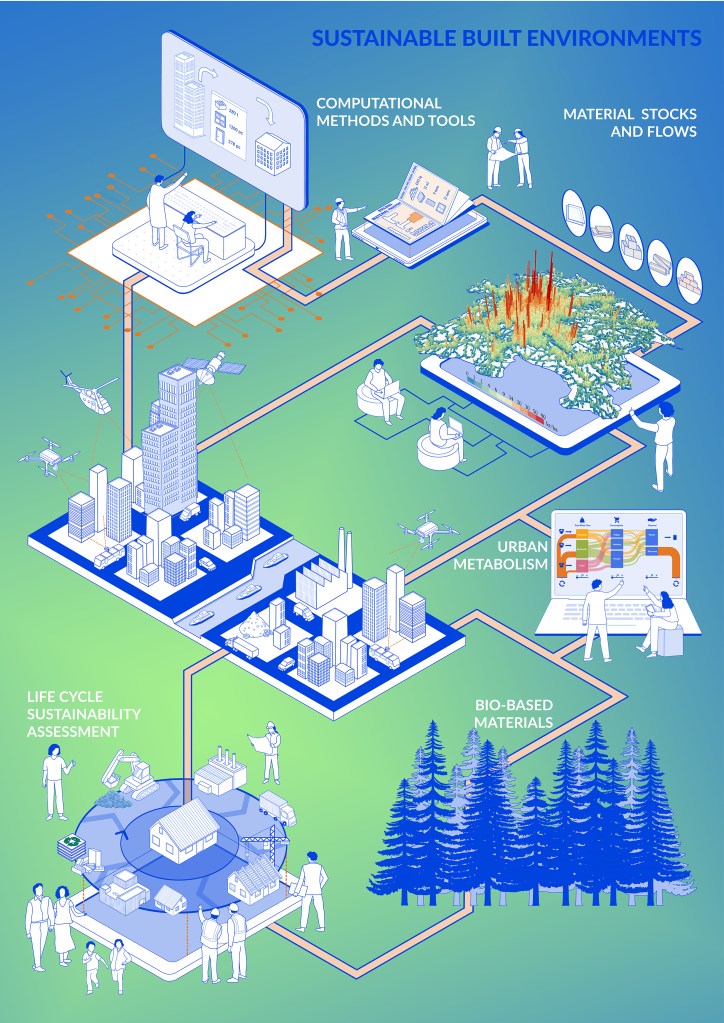
The Sustainable Built Environments Research Area focuses on developing methods, tools, and strategies to enhance the sustainability performance of the built environment. Our research encompasses everything from construction materials and building products to entire buildings, neighbourhoods, cities, and regions. We build upon and advance the foundations of sustainability science, while also engaging in applied research with a diverse range of stakeholders, including material manufacturers, designers, planners, and citizens.
News & Events
-
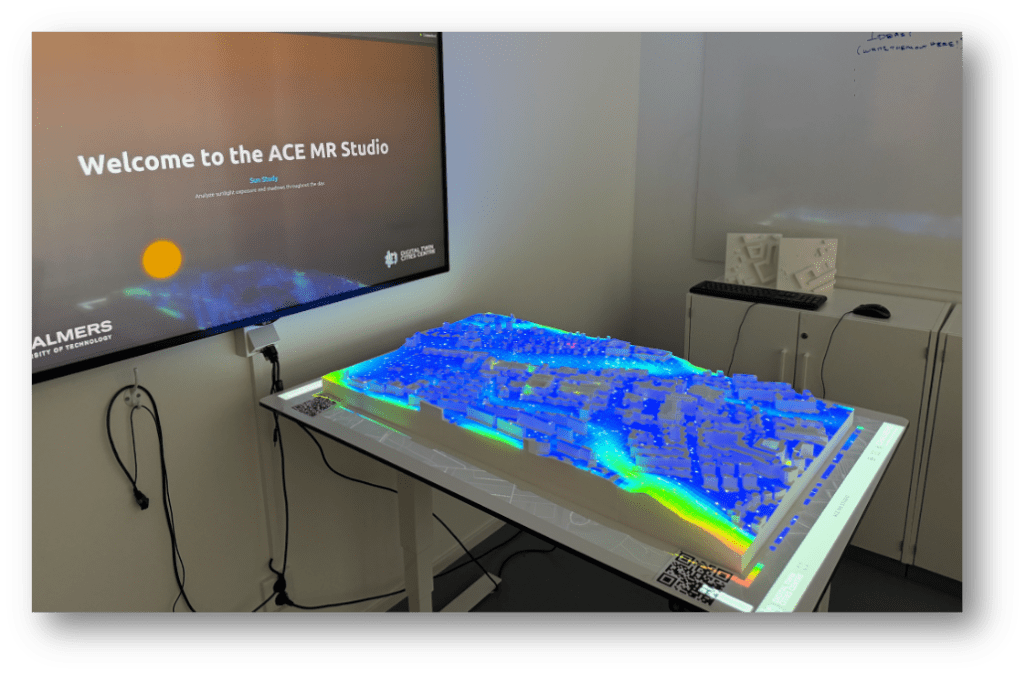
Creating the ACE Mixed Reality Studio
Complex urban simulations are often difficult to discuss collectively. Results live on individual screens, in reports, or PowerPoint presentations, making shared immersive interpretation challenging. The…
-
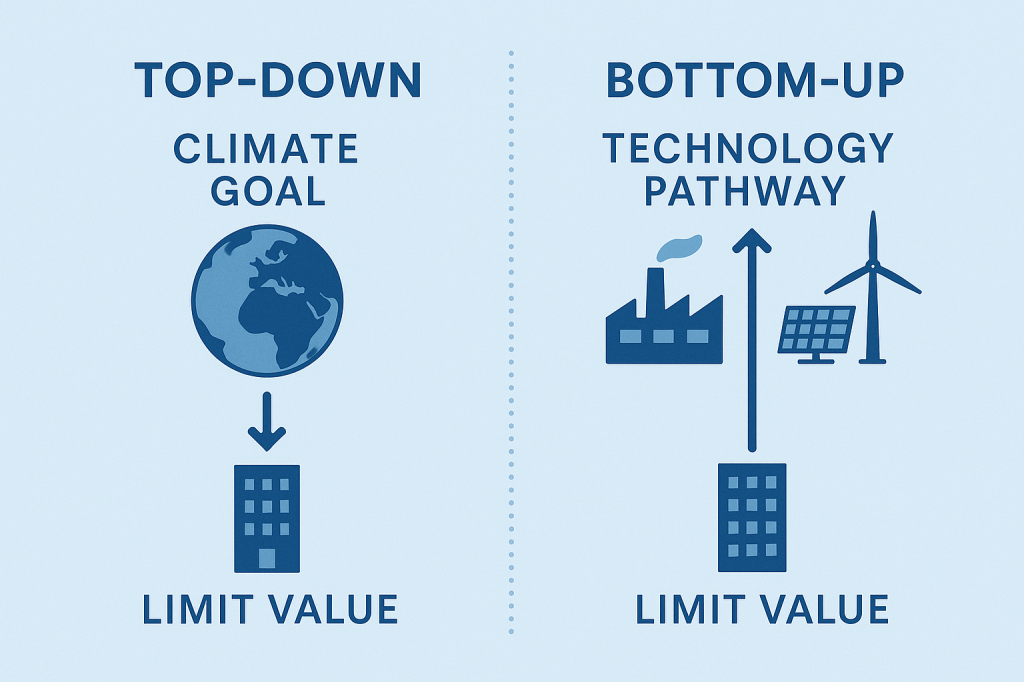
Interview: Reduction Roadmaps and Climate Limit-Values in Construction
As the construction sector works to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions, one tool is rapidly gaining importance: limit-values that define how much climate impact new…
-

Pragmatism in Practice – Interview with Sjouke Beemsterboer
Sjouke Beemsterboer discusses his PhD journey with us in this interview – research on life cycle assessment (LCA) in the Swedish building sector, and advice for…
Recent Projects
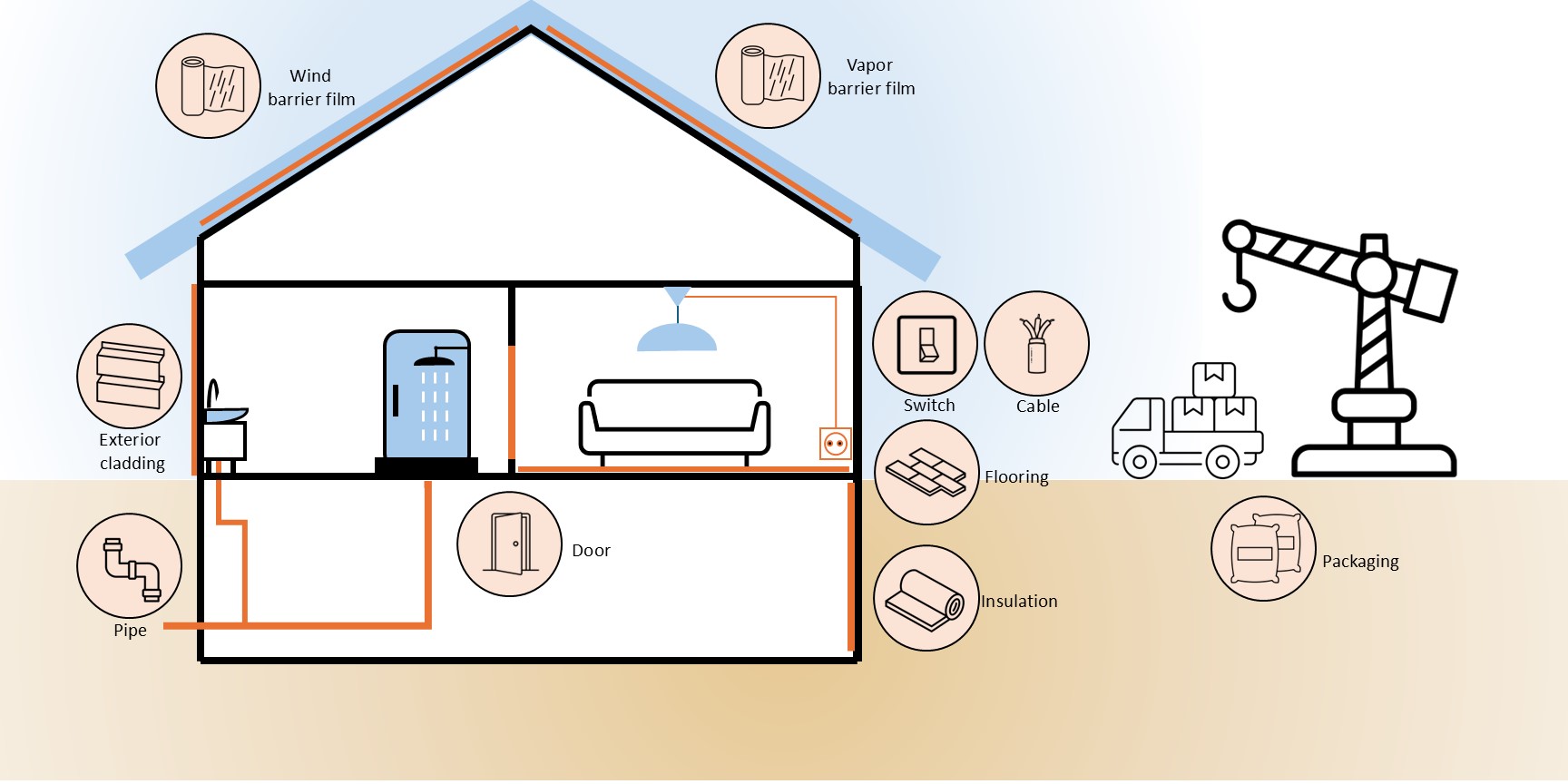
Improving plastic circularity in the construction sector
This project aims to improve plastic waste management at the construction sites to improve the plastic circularity, bringing the climate incentives into focus.

Exploring the material stock – urban form nexus for urban sustainability
This project uses a systems perspective to include, understand, and analyze interrelations between built environment material stocks, morphological types (e.g., buildings, roads), their spatial characteristics, the function they provide (e.g., shelter, transport), and socioeconomic and environmental implications of different urban forms. At the core of this project is the integration of two disciplines with a strong systems perspective tradition: built environment stock modeling and urban morphology

The development of buildings is an immensely carbon- and resource-intensive process and circular economy strategies are key to decrease the environmental impacts of the construction industry. In developed economies, extensive volumes of construction materials are stocked in existing buildings and ought to be reclaimed.
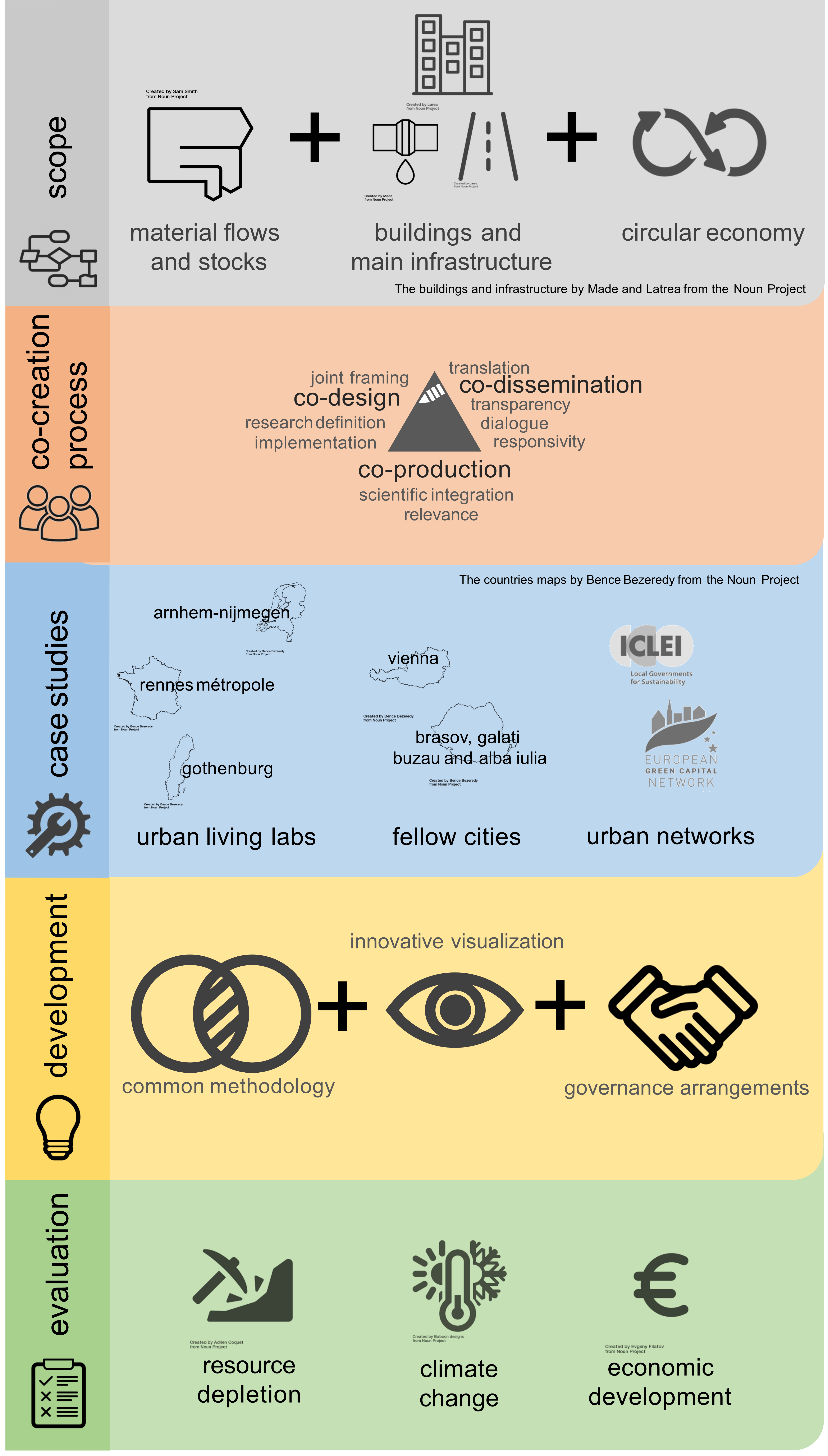
The CREATE project aims at supporting urban transformation processes towards the circular economy by making an inventory of the existing material stocks within urban construction, developing reliable scenarios for future expected material flows, and providing governance arrangements on how to approach the circular economy transition.

Architectural design variable assessment in multi-objective life cycle optimisation
This project aims to identify the important architectural design variables in early design stage for life cycle optimisation by interacting with stakeholders who have major influence in early design stage.

Digital material inventories for sustainable urban mining
This project develops a method to enable the reuse and recycling of urban construction materials using urban digital twins. By combining remote sensing, computer vision, and machine learning, it creates a detailed, dynamic inventory of material stocks to support circular economy strategies and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The approach advances life cycle assessment methods and will be tested through real-world case studies with stakeholder input.

